Kims Hospitals, Beside Vijaya Sales, Madinaguda
+91-7799111005
A shoulder dislocation occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) moves out of the shoulder socket (glenoid). The shoulder joint is the most mobile joint in the body, making it vulnerable to injuries. This condition can result from accidents, falls, or sports-related impacts. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for recovery and to prevent future dislocations.
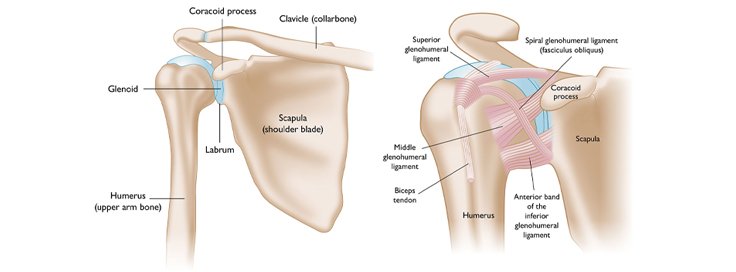
There are three main types of shoulder dislocations based on the direction of displacement:
Doctors use several methods to confirm a shoulder injury, including:
For recurrent shoulder instability, surgery may be necessary:
Recovery involves:
A dislocated shoulder is a painful but treatable condition. Early intervention, proper care, and strengthening exercises can reduce recurrence. If you experience symptoms, seek medical attention immediately to prevent further complications.
Madinaguda
Kims Hospitals,
Mon - Sat: 9 am - 9 pm,
Sunday: 10am - 2pm.
© All rights reserved by ARUN ORTHO CARE - Designed By Venlas Group.