Complicated Knee Fractures Treatment
Understanding Complicated Knee Fractures
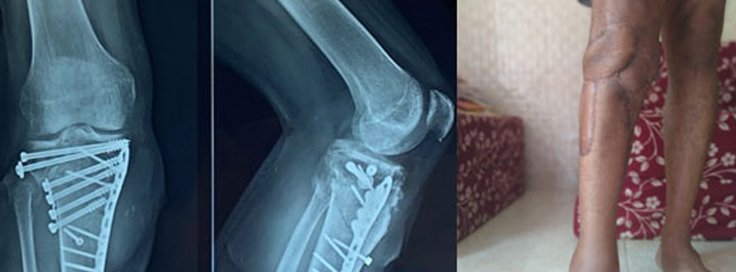
A complicated knee fracture is a severe injury involving multiple bone fragments, ligament damage, or joint misalignment. Unlike simple fractures, these injuries require specialized treatment to restore function and prevent long-term complications. Knee fracture treatment varies based on severity, with some cases requiring surgery and extensive rehabilitation.
Causes of Knee Fractures
Knee fractures occur due to high-impact trauma, such as:
Car accidents cause significant force on the knee joint.
Sports injuries, particularly in high-contact sports like football and basketball.
Falls from height, which can put excessive pressure on the knee.
Osteoporosis, weakening bones and making them more prone to fractures.
Common Symptoms of Knee Fractures
Recognizing the symptoms of a severe knee fracture is crucial for timely treatment. Key symptoms include:
Intense pain and swelling in the knee.
Difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg.
Visible deformity or misalignment.
Limited range of motion.
Bruising and tenderness around the knee.
Types of Knee Fractures
Several types of knee injuries and fractures can affect mobility and function, including:
Patellar fractures (kneecap fractures), often resulting from direct impact.
Distal femur fractures, affecting the lower part of the thigh bone.
Tibial plateau fractures, which involve the top portion of the shinbone.
Comminuted fractures, where the bone shatters into multiple pieces.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
A knee fracture specialist conducts a thorough evaluation using:
X-rays, to determine the extent of bone damage.
CT scans, offering a detailed view of complex fractures.
MRI scans, to assess soft tissue and ligament involvement.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Immobilization with braces or casts for minor fractures.
Physical therapy to restore mobility after healing.
Pain management with medications and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Surgical Treatment
Knee fracture surgery, such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF).
Minimally invasive knee surgery, reducing recovery time.
Bone grafting, for cases involving bone loss.
Total knee replacement, for severe fractures with joint damage.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-treatment knee fracture rehabilitation is crucial for regaining strength and function. This includes:
Physiotherapy for flexibility and muscle rebuilding.
Weight-bearing exercises to restore walking ability.
Lifestyle modifications, such as using supportive footwear.
Preventing Knee Fractures
To reduce the risk of serious knee fractures, follow these tips:
Strengthen leg muscles with regular exercise.
Use protective gear during sports.
Maintain bone health with a calcium-rich diet.
Avoid high-risk activities if you have osteoporosis.
When to See a Knee Fracture Specialist
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
Severe knee pain after an injury.
Inability to move or bear weight on the leg.
Noticeable knee deformity.
